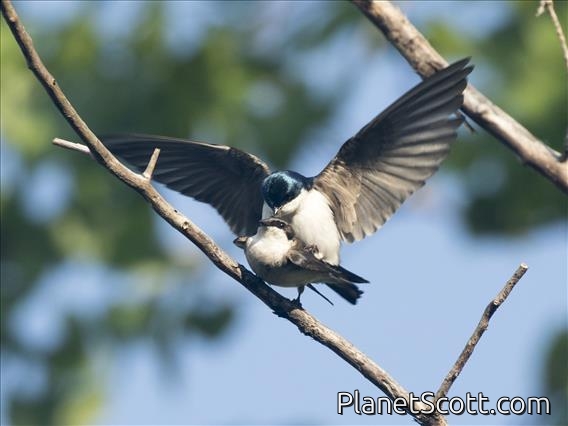
Tree Swallow (Tachycineta bicolor)
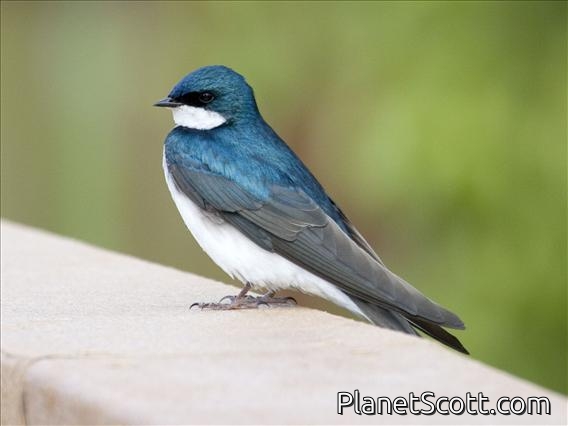






About Tree Swallow (Tachycineta bicolor)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Perching Birds
- Family: Swallows
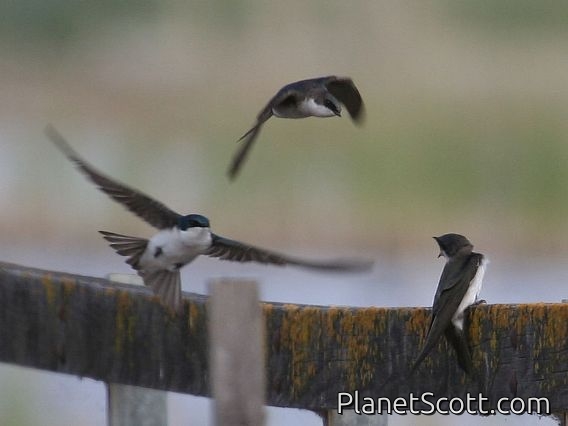
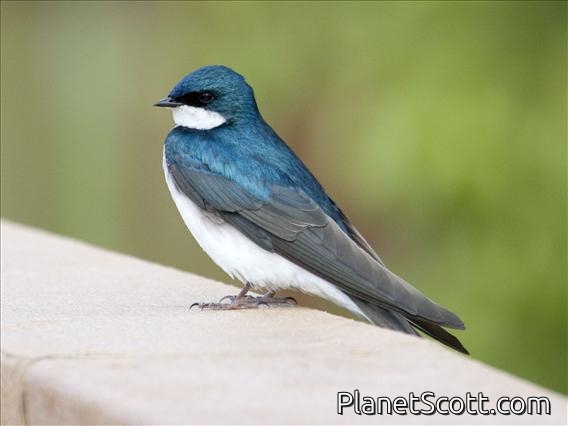
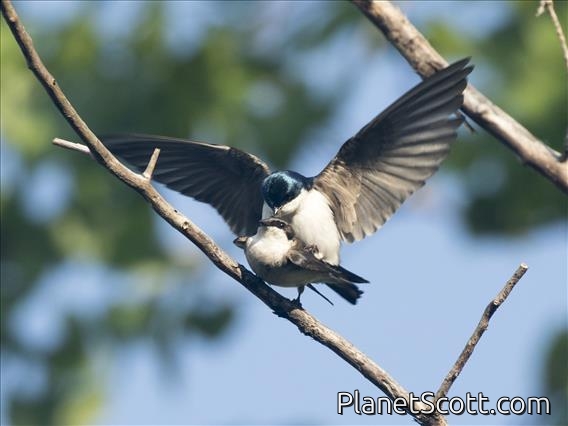
The tree swallow is a migratory bird of the family Hirundinidae. Found in the Americas, the tree swallow was first described in 1807 by French ornithologist Louis Vieillot as Hirundo bicolor. It has since been moved to its current genus, Tachycineta, within which its phylogenetic placement is debated. The tree swallow has glossy blue-green upperparts, with the exception of the blackish wings and tail, and white underparts. The bill is black, the eyes dark brown, and the legs and feet pale brown. The female is generally duller than the male, and the first-year female has mostly brown upperparts, with some blue feathers. Juveniles have brown upperparts, and gray-brown-washed breasts. The tree swallow breeds in the US and Canada. It winters along southern US coasts south, along the Gulf Coast, to Panama and the northwestern coast of South America, and in the West Indies.
Source: Wikipedia
Trips
Visits
-
2006-04-16
Kern National Wildlife Refuge, United States of America× -
2006-08-13
Canyonlands National Park, United States of America× -
2007-01-13
Suisun Marsh, United States of America× -
2007-03-06
Lake Merced , United States of America× -
2007-04-10
Ejido Lagoon, United States of America× -
×
-
2008-05-10
Lake Merced , United States of America× -
2009-01-16
Tulum, Mexico× -
2009-01-18
Lamanai Ruins River Trip, Belize× -
2009-01-28
Tikal, Guatemala× -
2009-05-08
Burnidge Forest Preserve, United States of America× -
2009-06-10
Effie Yeaw Nature Center, United States of America× -
2010-04-18
Point Reyes National Seashore, United States of America× -
2010-05-27
Kenai Peninsula, United States of America× -
2010-05-29
Potter Marsh, United States of America× -
2010-06-08
Talkeetna, United States of America× -
2010-06-08
Denali State Park, United States of America× -
2011-05-29
Del Puerto Canyon and Mines Road, United States of America× -
2012-06-01
Higgins Lake, United States of America× -
2012-07-08
Necedah NWR, United States of America× -
2012-07-09
Sax-Zim Bog, United States of America× -
2012-07-10
Bluestem Prairie, United States of America× -
2012-07-10
Arrowwood NWR, United States of America× -
2012-07-12
Yellowstone National Park, United States of America× -
2013-03-17
Lake Merced , United States of America× -
2013-04-19
Bolivar Peninsula, United States of America× -
2013-04-19
Anahuac NWR (UTC 049), United States of America× -
2013-07-02
Yolla Bolla Wilderness, United States of America× -
2014-02-22
Panoche Valley, United States of America× -
2014-02-22
Santa Fe Grade, United States of America× -
2014-03-04
Chabot Regional Park, United States of America× -
2014-04-05
Cosumnes River Preserve, United States of America× -
2014-04-06
Delta Meadows State Park, United States of America× -
2014-06-15
Golden Gate Park - North Lake, United States of America× -
2014-06-22
Redwood Valley, United States of America× -
2014-07-16
Nome, United States of America× -
2014-07-17
Nome--Safety Sound, United States of America× -
2014-07-18
Nome-Kougarok Road, United States of America× -
2014-07-19
Nome-Teller Hwy, United States of America× -
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×