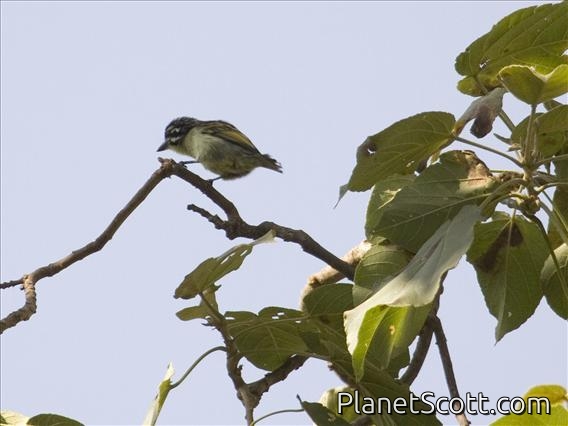
Yellow-fronted Tinkerbird (Pogoniulus chrysoconus)
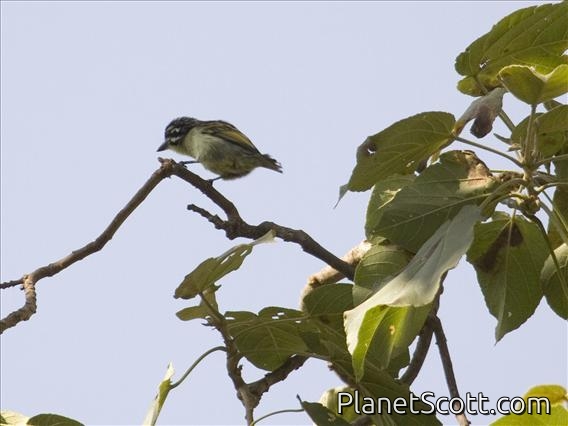

Yellow-fronted Tinkerbird (Pogoniulus chrysoconus)
×


Yellow-fronted Tinkerbird (Pogoniulus chrysoconus)
About Yellow-fronted Tinkerbird (Pogoniulus chrysoconus)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Woodpeckers, Barbets, Toucans, and Puffbirds
- Family: African Barbets
The yellow-fronted tinkerbird is a small bird in the family Lybiidae formerly known as yellow-fronted tinker barbet. It is sometimes considered conspecific with its southern counterpart, the red-fronted tinkerbird, Pogoniulus pusillus. Barbets are near passerine birds with bristles around the base of the bill and a world-wide tropical distribution.
Source: Wikipedia
Visits
-
2003-01-15
Etosha National Park, Namibia× -
2011-01-12
Wondo Genet, Ethiopia×